In the fast-paced world of engineering, the design of turbomachinery stands at the forefront of technological innovation. These powerful devices, which include turbines, compressors, and pumps, play a crucial role in various industries, from aviation and energy generation to automotive and manufacturing. The efficiency, performance, and reliability of turbomachinery are paramount, and achieving optimal design is a complex endeavour. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating realm of turbomachinery design methodology, exploring the key steps and considerations that drive progress in this field.
The Significance of Turbomachinery:
Turbomachinery is the beating heart of many industrial processes and systems. These devices convert energy between mechanical and fluid forms, propelling airplanes through the sky, generating electricity, and facilitating countless other applications. Efficiency and performance are of the essence, with small improvements in design leading to significant advancements in energy conservation and productivity.
The Design Process:
- Requirements Analysis: The journey begins with a comprehensive understanding of the application’s requirements. Design engineers must consider factors such as flow rates, pressure differentials, and temperature ranges to meet the needs of the specific industry.
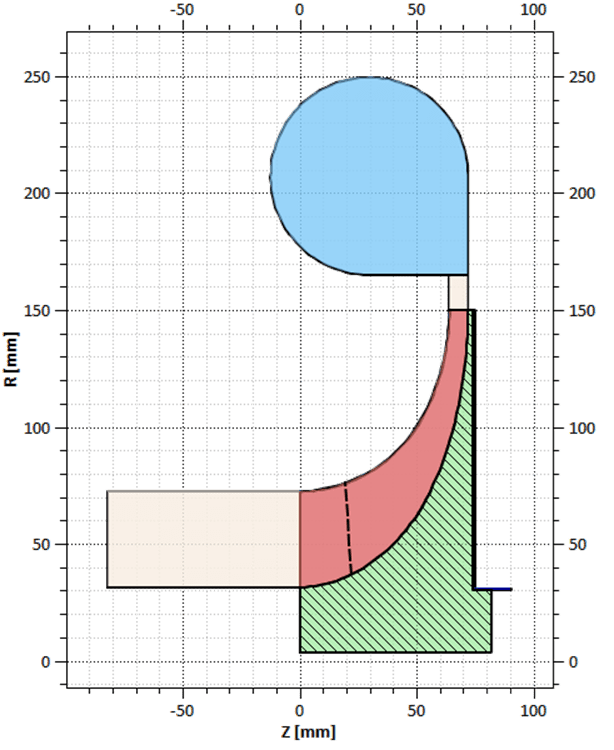
- Conceptual Design: At this stage, various design concepts are explored. Engineers consider factors like impeller design, blade profiles, and flow path geometries to determine which concept is most promising.
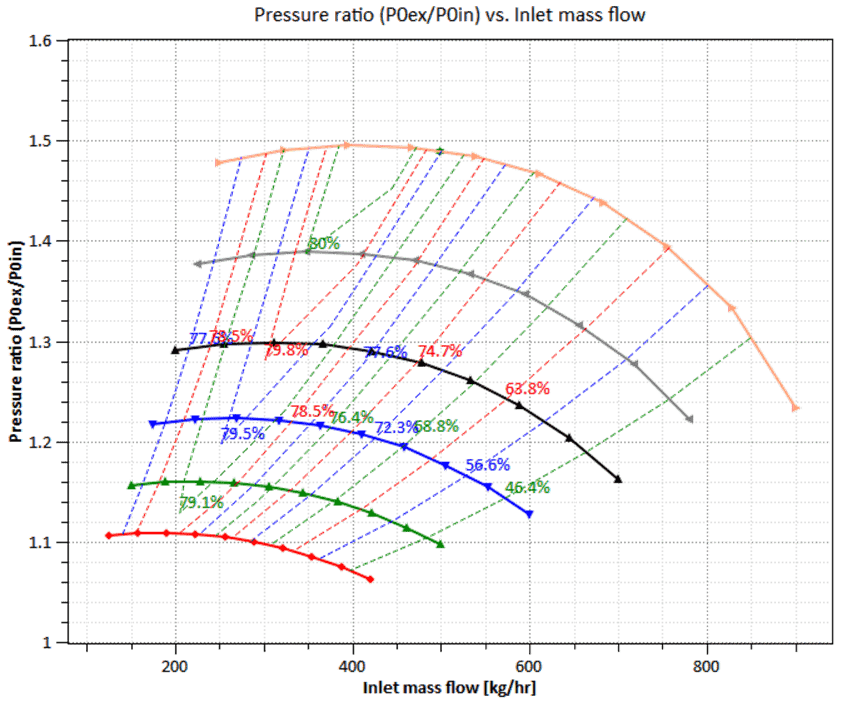
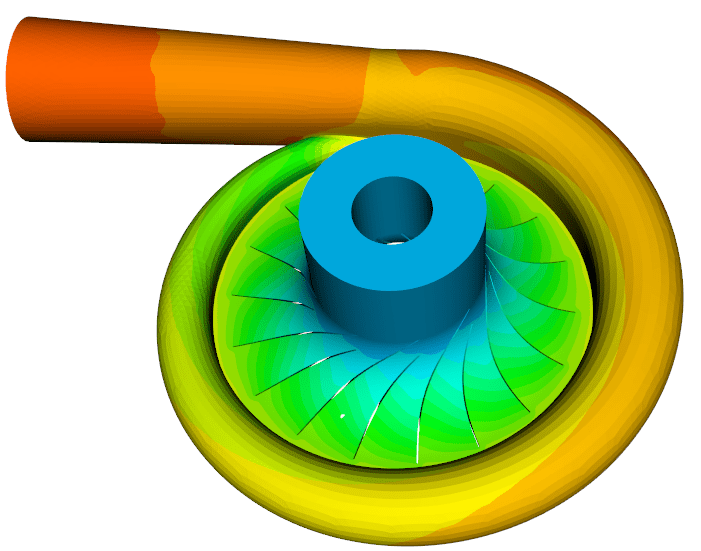
- Numerical Simulations: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) plays a pivotal role in the design process. Engineers employ CFD simulations to predict how different designs will perform under various conditions, enabling them to refine the concepts further.
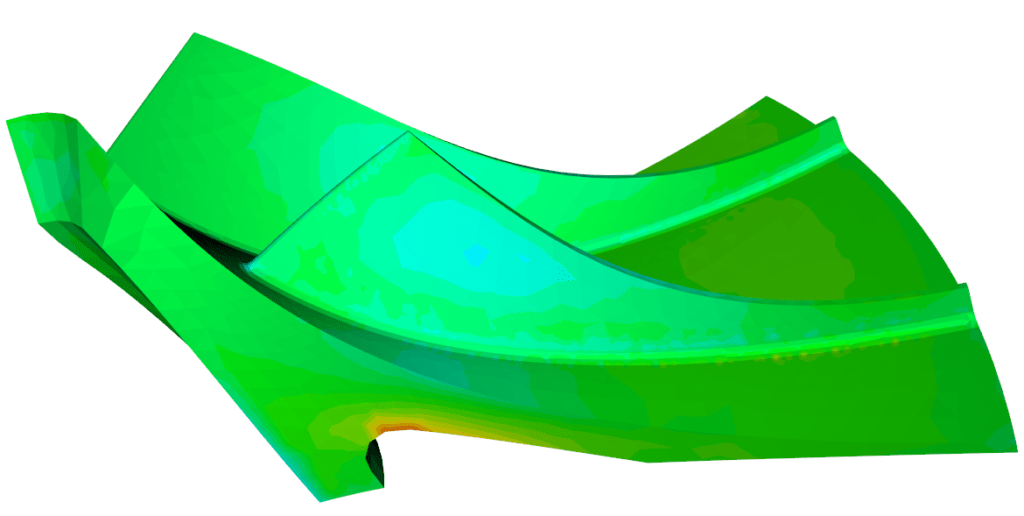
- Prototyping: Physical prototypes are built based on the most promising design concepts. These prototypes are then rigorously tested to verify the accuracy of the CFD predictions and to fine-tune the design.
- Materials and Manufacturing: The choice of materials and manufacturing methods is critical. Components need to withstand high temperatures, pressures, and rotational forces while maintaining efficiency.
- Testing and Validation: The final design is tested in real-world conditions to validate its performance. This often involves a series of bench tests and may even include field tests in the application environment.
The Role of Computational Tools:
The use of advanced software tools, such as those offered by DESiM Innovations (TurboTides, Cycle-Tempo, EnnovaCFD and TCAE by CFDSupport), has revolutionized turbomachinery design. These tools enable engineers to perform intricate simulations, optimize designs, and predict performance accurately. The iterative nature of design is significantly enhanced through the use of these tools, allowing engineers to explore a broader range of design parameters quickly.
Challenges and Future Trends:
Turbomachinery design faces several challenges, including ever-increasing efficiency demands, environmental concerns, and the need for compact designs. Emerging technologies, such as additive manufacturing and smart materials, are poised to transform the industry, enabling the creation of more efficient and robust turbomachinery.
In conclusion, turbomachinery design is an art that balances science and engineering. The methodologies employed are the result of decades of innovation and continue to evolve with advancements in technology. As we move towards a more energy-conscious and eco-friendly world, the significance of designing efficient turbomachinery cannot be overstated. The future promises exciting developments in this field, driven by engineers who are committed to pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
